When choosing between a single-compressor and a dual-compressor system for freezers, it helps to understand how they operate. Each type of compressor system has their own unique features along with pros and cons. This article thoroughly explains the differences between single vs dual-compressor systems, how they operate and the benefits & disadvantages of each.
Single-Compressor Systems in Freezers:
Single-compressor systems operate just like their name states, with just one cooling cycle. This is similar to a typical household freezer. In these units, one compressor cools the entire freezer, which makes the design more simple and often more affordable.
However, the downside of a single-compressor unit is the freezer relies solely on that compressor. With that said, if that one compressor fails, the freezer can’t maintain its temperature and risks damaging the product stored within the freezer.
Additionally, in single-compressor freezers, the compressor is constantly running. This can lead to more wear and tear and ultimately a shorter lifespan.
Pros of Single Compressors:
- Lower Initial Cost: Single-compressor freezers are generally more affordable.
- Simplicity: Fewer components mean simpler operation and fewer potential points of failure.
- Compact Design: These systems often take up less space due to the single compressor setup.
- Lower Noise: With only one cooling cycle, single-compressor units can be quieter compared to dual-compressor systems.
Cons of Single Compressors:
- Shorter Lifespan: The single compressor works harder and can wear out faster, reducing the overall lifespan of the unit.
- No Backup: If the compressor fails, the freezer loses its cooling ability entirely, risking the loss of stored items.
- Less Temperature Precision: Maintaining colder temperatures, such as an ultra-low temperature freezer, is harder for a single compressor, and fluctuations are more common.
- Increased Wear and Tear: Constant operation can lead to overheating, which accelerates the wear on the compressor.
Dual-Compressor Systems in Freezers:
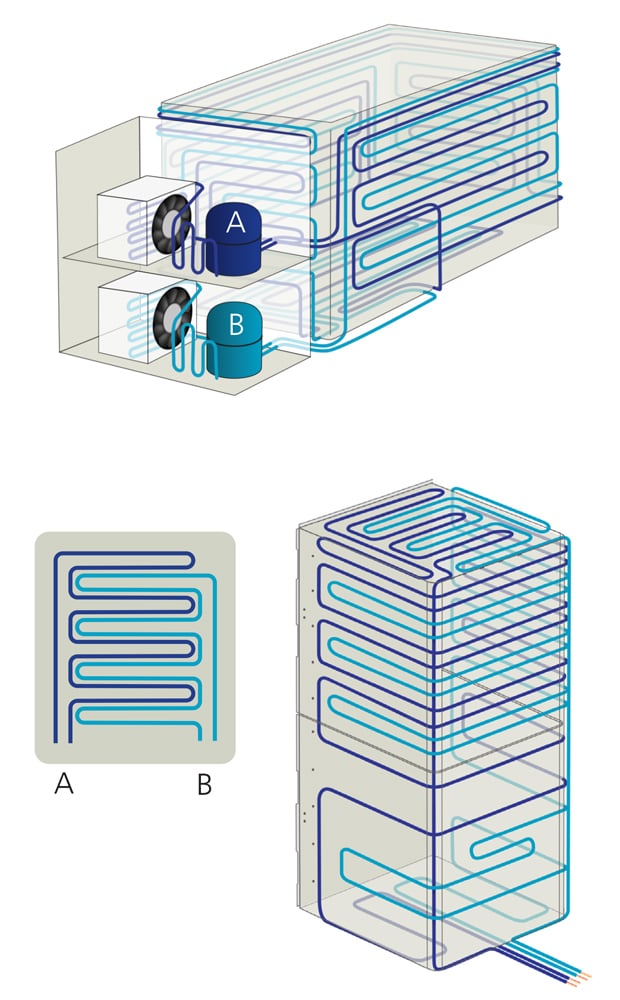
A dual-compressor system houses two compressors working in a cascade cycle.
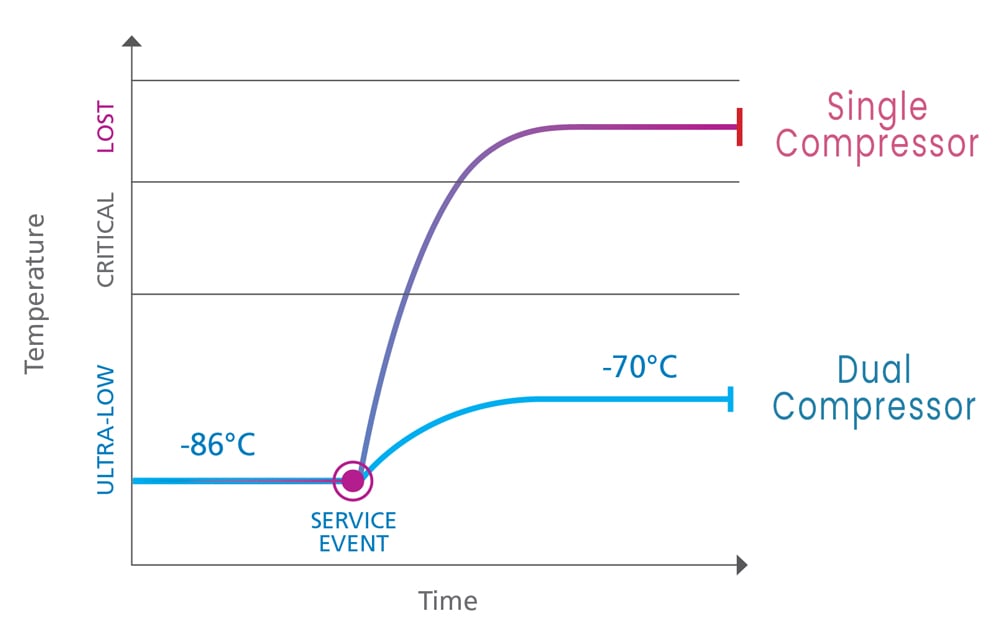
Here’s how a dual-compressor system works: there are two separate compressors where one of the compressors handles higher temperatures, and the other manages lower temperatures. This two-cycle process allows the freezer to reach the set temperatures efficiently and provide more stable temperatures than a single-compressor. If one compressor fails, the freezer may still be able to maintain a low temperature. Although, it may not be as cold as usual, this still allows the freezer to protect the samples/product stored within rather than the unit warming up to temperatures that would be too high for the samples.
With that said, in some dual-compressor systems, one compressor might serve as a backup in case of failure, while in others, both work together to maintain temperatures. This redundancy means increased reliability.
Pros of Dual Compressors:
- Longer Lifespan: Since the workload is shared between two compressors, they experience less wear and tear.
- Backup Capability: Even if one compressor fails, the system can continue running at a slightly higher temperature.
- Better Temperature Control: Dual compressors help maintain consistent, ultra-low temperatures, reducing the risk of freezer burn or temperature fluctuations.
Cons of Dual Compressors:
- Higher Noise Levels: Since there are two active cycles, these units may be noisier, though good design can minimize this.
- Cost: Dual-compressor freezers tend to be more expensive, but the investment can pay off with a longer unit lifespan.
As stated in this article single vs dual-compressor systems have many differences, with each providing their own benefits but also have specific disadvantages as well. In short, dual-compressor systems offer better reliability and longevity, especially for those needing ultra-low temperatures and storing sensitive samples. Single-compressor units on the other hand are initially more affordable but may have a shorter lifespan. Your specific needs, like budget, what you’re storing, temperature requirements, and backup capabilities should all be considering when choosing a freezer. We always recommend you consult with a highly qualified LabRepCo cold storage specialist before deciding on which freezer is best for you.
For more information on freezers contact us below and speak with your local LabRepCo sales rep today or visit our freezers section for a variety of options.